To power a well pump on backup, you need to install an inverter that matches the pump’s voltage and handles its startup surge, along with a reliable battery system such as lithium-iron phosphate. You should also set up a transfer switch or relay system for safe switching between main power and backup sources. Proper wiring, safety devices, and regular maintenance are essential for dependable operation. If you want to know the step-by-step process, you can explore more details here.
Key Takeaways
- Determine the pump’s power requirements and select an inverter or generator capable of handling startup surges and continuous load.
- Install a transfer switch or automatic transfer switch (ATS) to safely switch between main power and backup sources.
- Use appropriately rated wiring, protective devices, and safety measures following electrical codes for reliable backup operation.
- Incorporate a solar, battery, or hybrid system with charge controllers and relays for seamless, renewable backup power.
- Regularly test and maintain the backup system, including batteries, connections, and automatic switching components, for dependable water supply.
Assessing Your Well Pump Power Needs
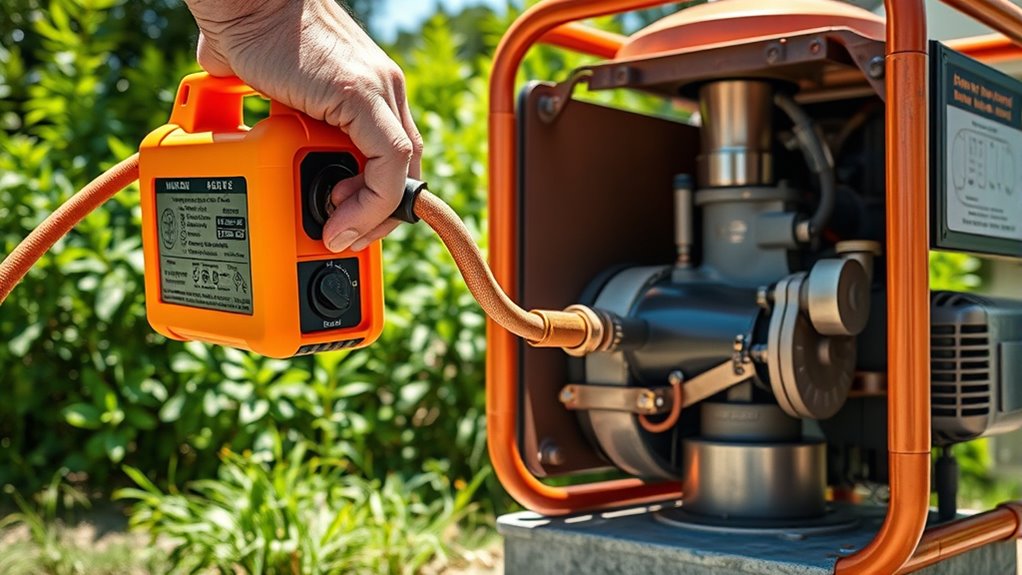

To effectively power your well pump during an outage, you first need to assess its specific power requirements. Well pumps typically range from ½ HP to 2 HP, with power consumption proportional to size. A ½ HP pump uses about 700 to 1,000 watts, while a 1 HP pump consumes between 1,500 and 2,000 watts during normal operation. Remember, starting wattage can be two to three times higher, often requiring 2,000 to 3,500 watts for larger pumps. Check your pump’s voltage—most run at 120V or 240V—and note the amperage, which varies with horsepower. Larger pumps demand higher-capacity circuit breakers and thicker wiring. The starting wattage is significantly higher than running wattage, which is crucial to consider when selecting a generator or backup power system. Properly estimating peak power needs ensures your backup system can handle all operational demands without failure. Additionally, ensuring your backup system maintains a high vibrational energy level can improve overall performance and longevity of your equipment. Considering AI-driven diagnostics can help monitor and optimize your backup power setup over time.
Exploring Solar Backup Systems for Well Pumps
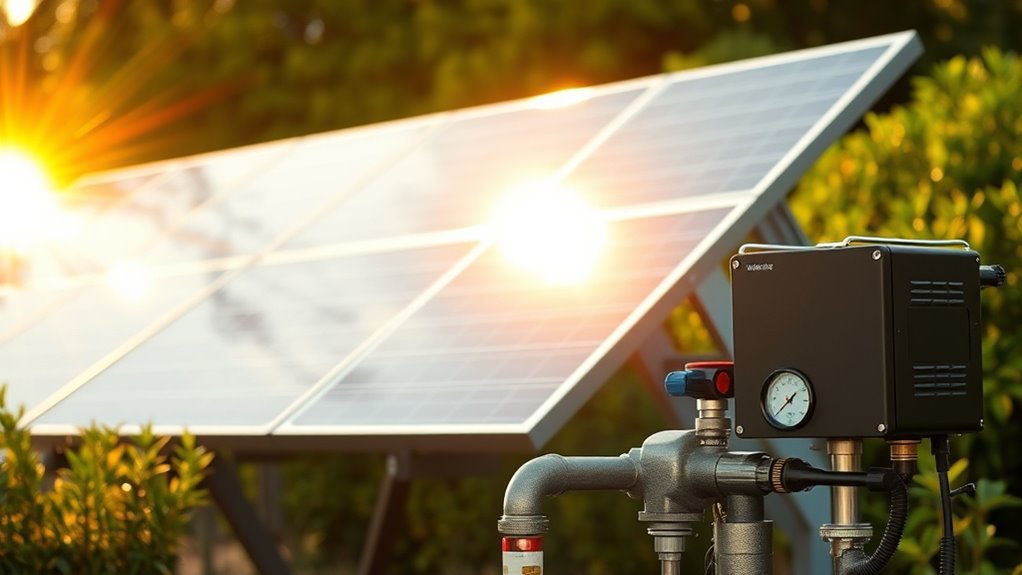

Have you considered using a solar backup system to power your well pump during outages? Solar systems include panels that convert sunlight into DC electricity, which can directly run the pump or charge batteries for later use. Battery banks store this energy, ensuring your pump keeps working during cloudy days or at night. An inverter then converts the stored DC power into AC, compatible with most well pumps. Charge controllers prevent batteries from overcharging, and sensors monitor sunlight levels to protect the pump from damage when sunlight is low. Proper installation involves secure electrical connections, strategic placement of control boxes and sensors, and effective cable management. This setup reduces reliance on grid power, lowers long-term costs, and offers a renewable, reliable backup solution for continuous water access. Understanding the components of solar well pump systems enhances installation efficiency and reliability].
Choosing the Right Inverter and Battery Setup

Choosing the right inverter and battery setup is essential for reliable backup power for your well pump. You need an inverter that can handle the pump’s startup surge and continuous running wattage. Selecting batteries with sufficient capacity ensures you have enough backup time, with LiFePO4 batteries preferred for their longevity and high usable capacity. To optimize your system, consider these key points:
- Match the inverter’s surge capacity to the pump’s startup wattage to prevent overloads.
- Use batteries sized based on your pump’s power needs, aiming for at least 2,048 watt-hours, scalable to 6,144 watt-hours.
- Opt for a 24V or 48V battery system to improve efficiency and accommodate higher loads.
- Incorporate safety features such as overcurrent protection and proper grounding to safeguard your setup.
- Ensure your inverter has a properly rated AC output that matches your well pump specifications to maintain consistent operation. Additionally, selecting a system with reliable components can significantly reduce the risk of failure during critical times.
A well-matched inverter and battery setup guarantees smooth operation during outages and prolongs system lifespan.
Installing Backup Power Components Safely and Effectively
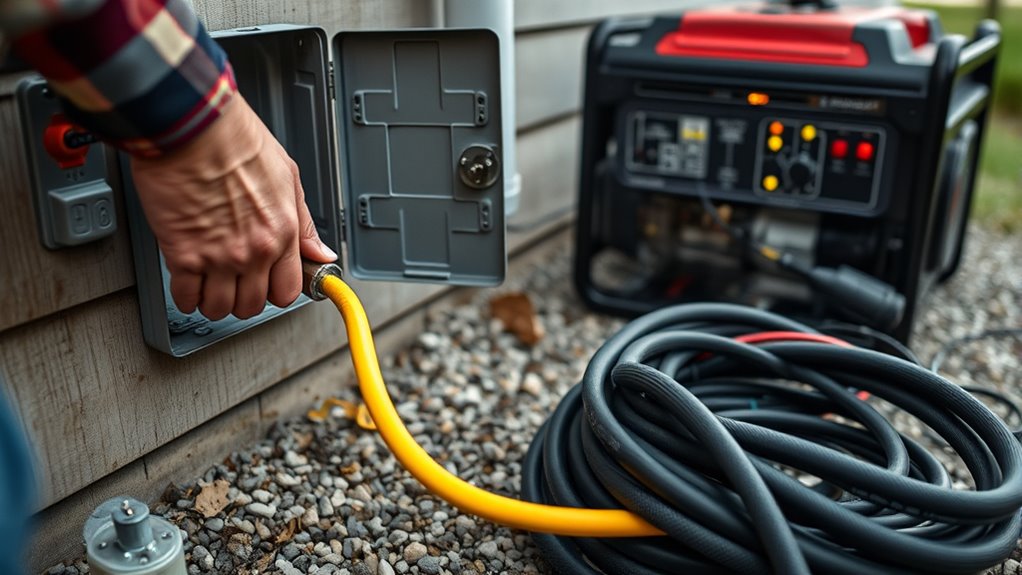

Ensuring your backup power components are installed safely and effectively is essential for reliable operation and personal safety. First, install proper circuit breakers and fuses to protect wiring and components from overloads and short circuits. Use a mechanical interlock on the main breaker panel to prevent back-feeding power to utility lines when running on backup. Ground all system parts according to local electrical codes to avoid shocks and reduce electrical noise. Make sure wiring is rated for your pump’s voltage and current. Separate utility and backup circuits with dedicated panels, and use a transfer switch or ATS for safe switching. Enclose batteries and electrical components in weatherproof, ventilated boxes, and secure cables to prevent damage. Follow NEC guidelines, obtain permits, and schedule regular inspections for safe, reliable operation. Proper electrical safety measures are crucial to prevent accidents and ensure long-term system performance. Additionally, understanding the electrical safety standards can help ensure compliance with local regulations and improve overall system reliability. Incorporating proper grounding techniques can further enhance system safety and reduce the risk of electrical faults.
Calculating Power Requirements and Ensuring Proper Sizing
To guarantee your backup power setup works reliably, you need to accurately calculate your well pump’s power needs. This involves identifying the pump’s running and starting wattages and choosing an inverter that can handle these loads comfortably. Proper sizing prevents system overloads and keeps your well functioning during outages. Additionally, understanding the importance of space optimization and organization can help you set up your backup system efficiently in your utility area. Ensuring your system includes appropriate safety features is also crucial for safe operation and longevity of the equipment. Recognizing the impact of father-daughter bond can inspire a sense of protection and support when designing your system, emphasizing reliability and care. Furthermore, considering system maintenance is essential to keep your backup power system running smoothly over time.
Determining Pump Power Needs
Calculating the power requirements for your well pump is essential to select the right backup system. First, determine your pump’s horsepower and convert it to watts—0.5 HP equals about 375-960W, while 1 HP ranges from 746-1,920W. Second, check your pump’s voltage and current; most operate on 240 volts, with amps varying from 4 to 12 depending on size. Third, consider startup surge—starting watts can be 2 to 3 times the running watts, so plan for peak power demands. To guarantee proper sizing, focus on these points:
- Match the backup system’s wattage capacity with your pump’s running and starting power.
- Account for well depth and pump type, as they influence energy needs.
- Include safety margins for startup surges to prevent system overloads.
- Proper sizing ensures reliable operation and prevents potential damage to your backup system. Additionally, understanding the power requirements helps optimize energy efficiency and system longevity. Recognizing the importance of proper system sizing can prevent costly repairs and ensure consistent water supply during outages.
Selecting Appropriate Inverter
Choosing the right inverter size is essential to reliably power your well pump during outages. You need to account for both startup surge and continuous running wattage. Well pumps can draw 4–6 times their running current during startup, so oversize your inverter’s surge capacity by at least 50% to prevent voltage dips and shutdowns. Also, add a 10–20% margin to the continuous rating for inverter losses and other loads. When selecting an inverter, match the voltage and phase requirements of your pump. For example, a 230 VAC, single-phase pump needs compatible output. Proper sizing guarantees reliable startup and operation, avoiding overloads or damage. Ensuring your wall organization system is well designed can also help in managing the overall electrical setup efficiently. Additionally, considering the advanced inverter technology available can improve overall efficiency and protection for your equipment. Incorporating proper wiring techniques can further enhance safety and performance of your backup power system. Moreover, understanding the power factor of your pump can influence the sizing and efficiency of your inverter selection.
Wiring and Connecting Your Backup System
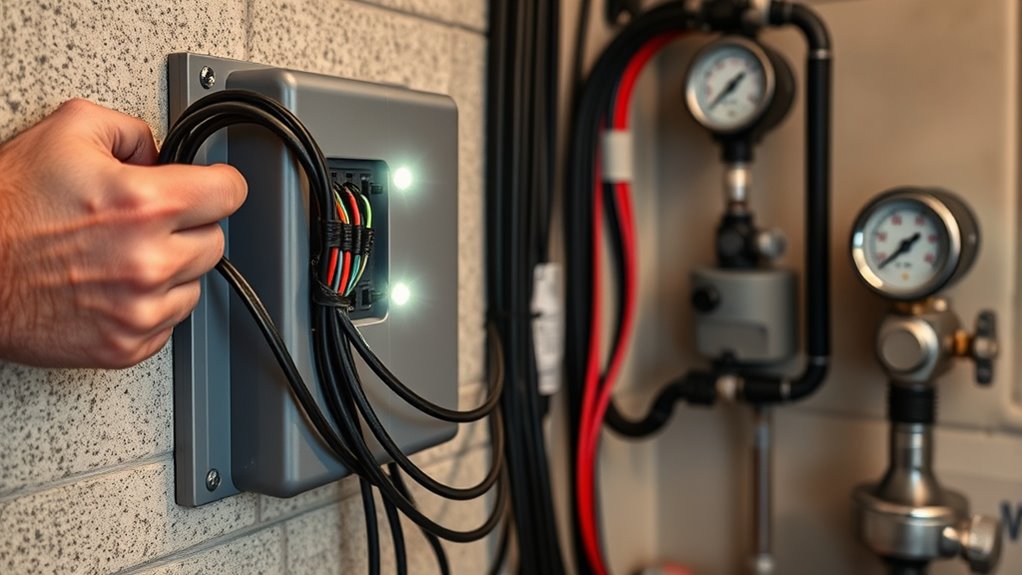

Before wiring your backup system, you must turn off all power at the electrical panel and pump control box to prevent electrocution or damage. Confirm the power is off with a voltmeter before proceeding. Follow NEC and local codes strictly to ensure safety and compliance. Use proper PPE and insulated tools to protect yourself during installation. Proper wiring and connection are critical for system safety and functionality.
Verify you:
- Match wiring color codes—red to red, yellow to yellow, black to black—according to your pump’s manual.
- Secure all wire splices with water-resistant kits and electrical tape for wet environments.
- Use copper wiring rated for your system’s voltage and current, with proper grounding to metal plumbing or motor frames to prevent shocks or damage.
Implementing Redundant and Hybrid Power Strategies
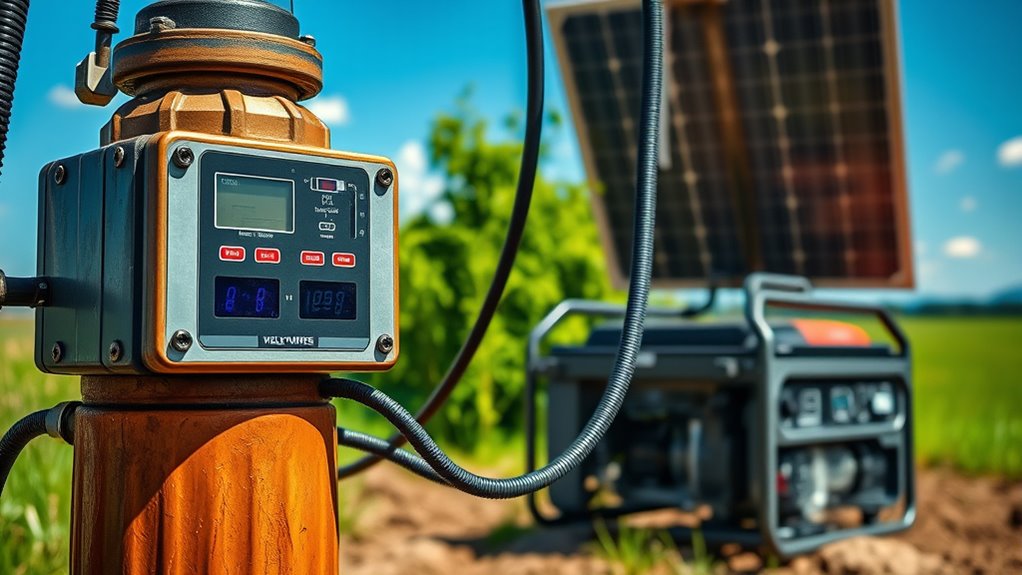

You can improve your well pump’s reliability by combining multiple power sources, such as solar, wind, or generators, into a hybrid system. Automated backup pumps switch seamlessly between power sources to prevent disruptions. Implementing these strategies guarantees your water supply remains consistent, no matter the situation.
Multiple Power Source Integration
Integrating multiple power sources to run a well pump enhances reliability and guarantees continuous operation during outages or fluctuations. You can do this by using relays or contactors to switch between sources, ensuring one failure doesn’t stop the pump. Employ three or more switches connected to relays for control from different sources. When designing your system:
- Choose relays with appropriate amperage and voltage ratings to handle your pump’s power safely.
- Ensure circuits prevent back-feed or cross-connection, avoiding damage.
- Recognize that manual or semi-automatic relay setups require careful wiring but aren’t fully automatic.
This approach provides flexibility and redundancy, keeping your water supply steady even if one power source drops out. Proper design and safety measures are essential for reliable operation.
Backup Pump Automation
Implementing backup pump automation guarantees your well remains functional during power outages by using redundant and hybrid power strategies. Automated systems switch seamlessly between power sources, such as batteries, solar, or grid electricity, ensuring continuous water supply. Lithium-iron phosphate batteries offer long-lasting, safe energy storage, often exceeding 15 years with thousands of charge cycles. Solar arrays integrated with these batteries allow for sustainable, off-grid operation, reducing reliance on the grid. Sensors like pressure switches and float levels monitor system status and trigger automatic switching, minimizing manual intervention. Hybrid solutions combine solar, batteries, and generators, providing flexibility and resilience. Automated controls streamline operation, prevent downtime, and safeguard your water system during outages or mechanical issues, making your well pump more reliable and efficient.
Maintaining and Testing Your Backup Power System
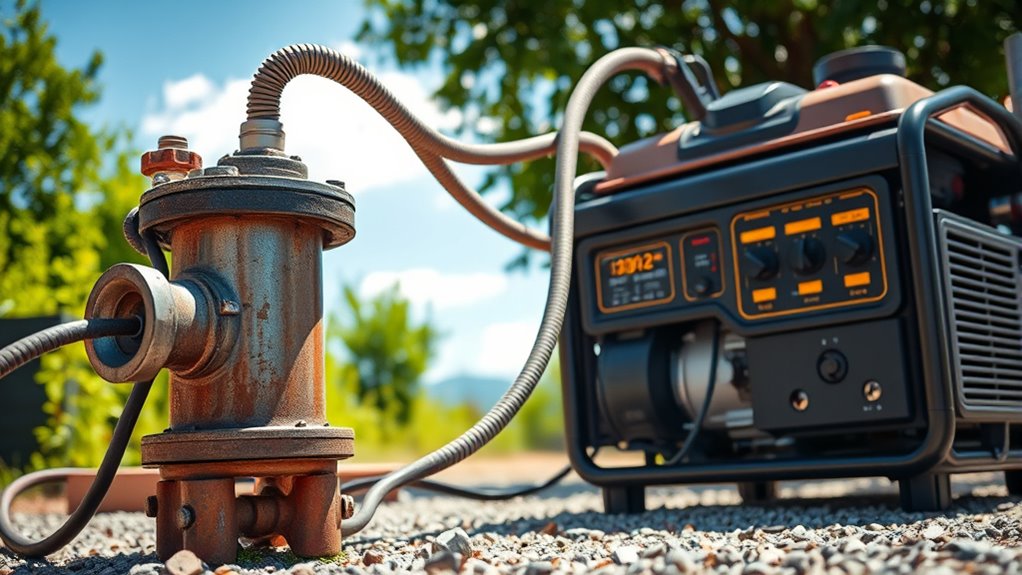

Regularly inspecting and testing your backup power system is essential to guarantee it functions reliably when needed. Consistent checks help identify issues before an outage occurs. To stay prepared, you should:
Routine inspections ensure your backup systems perform reliably when needed.
- Test your batteries and generators monthly, ensuring they hold a charge and start properly.
- Inspect electrical connections, wiring, and surge protectors for corrosion or damage.
- Use water pressure gauges regularly to monitor flow and pressure, catching potential pump or tank problems early.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Can My Backup System Run During a Power Outage?
Your backup system’s runtime depends on your battery capacity, pump demand, and surge needs. With a properly sized inverter and batteries of 1-2 kWh, you might get a few hours of operation, especially during short outages. For longer outages, larger batteries, solar recharging, or a generator can extend runtime. Regular testing guarantees your backup system performs effectively when you need it most.
What Maintenance Is Required for Solar and Inverter Backup Systems?
You might think maintenance is complicated, but it’s straightforward. Regularly clean your solar panels every 3-6 months to boost efficiency and check wiring for corrosion. Test your inverter every three months and keep its cooling system clean. Monitor your batteries’ voltage and replace them when capacity drops. Ensuring proper electrical connections, inspecting control systems, and lubricating pumps keep everything running smoothly and extend your system’s lifespan.
Can I Add Backup Power to an Existing Well Pump Setup?
Yes, you can add backup power to your existing well pump setup. You’ll need to evaluate your pump’s horsepower and electrical requirements, then select a compatible backup system like solar, generator, or manual pump. Wiring should be straightforward, often with plug-and-play connections, and automatic transfer switches can help switch between power sources seamlessly. Proper sizing and professional installation ensure reliable backup, keeping your water supply uninterrupted during outages.
How Do I Protect My System From Power Surges or Lightning Strikes?
To protect your system from power surges and lightning strikes, you should install surge arresters at critical points like the wellhead, pump control box, and main service panel. Use Type 3 lightning arresters to divert high-voltage surges safely to ground. Ground your system properly with deep well casings and copper grounding wires. Additionally, consider voltage stabilizers and unplugging electronics during storms to minimize damage. Regular maintenance also helps guarantee your protections stay effective.
What Are the Costs Associated With Installing a Backup Well Pump System?
Think of installing a backup well pump system as building a sturdy bridge across a turbulent river. Costs vary like the stones in the water—initially, you might spend $1,000 to $6,000 depending on pump type, installation complexity, and extras like permits or electrical work. Professional labor adds $500 to $1,500, and ongoing expenses include battery replacements and maintenance. Your total investment depends on your well depth, chosen backup power, and regional prices.
Conclusion
By carefully evaluating your needs and choosing the right backup system, you can guarantee your well pump keeps running when power outages strike. Remember, a stitch in time saves nine—regular maintenance and testing keep your backup ready to go. With proper planning and installation, you’ll enjoy peace of mind knowing your water supply is protected. Don’t wait until you’re caught in the dark—prepare now to keep your well flowing no matter what.










