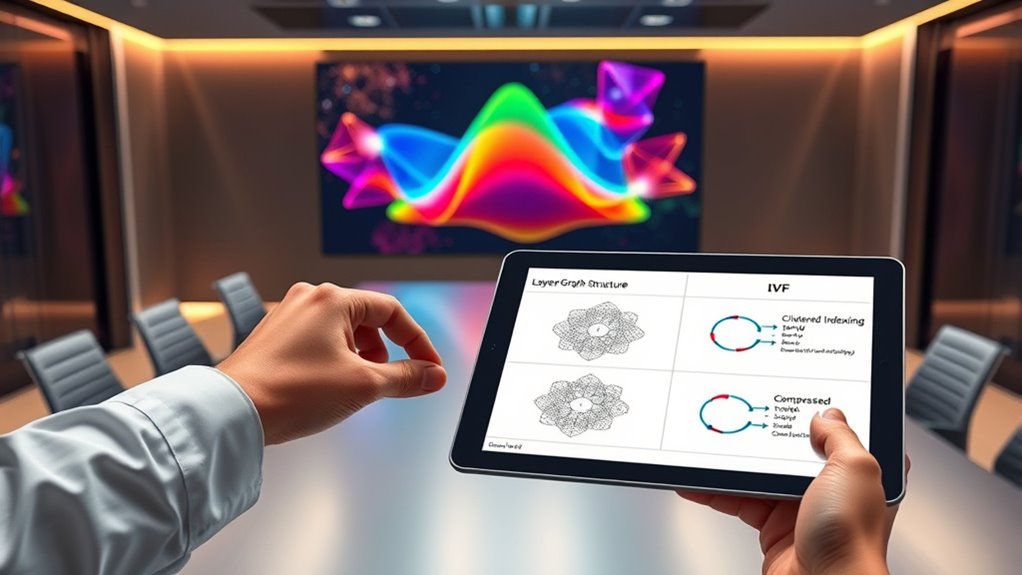
HNSW organizes data into a layered graph, enabling quick approximate searches by steering from coarse to fine details, making it scalable for large datasets. IVF clusters data into smaller groups, reducing search scope and speeding up queries, especially in massive collections. PQ compresses vectors into small codes, allowing fast distance calculations with minimal memory use. If you want to understand how these algorithms compare and work together, exploring further will reveal more insights.
Key Takeaways
- HNSW builds a layered graph for efficient approximate nearest neighbor searches, balancing speed and accuracy in high-dimensional spaces.
- IVF partitions datasets into clusters, reducing search scope by focusing on relevant cells instead of the entire dataset.
- PQ compresses vectors into compact codes, enabling fast, memory-efficient distance computations suitable for large datasets.
- HNSW dynamically adjusts connections across layers to maintain scalability as dataset size grows.
- IVF and PQ are often combined to improve search speed and memory efficiency in large-scale vector databases.
Have you ever wondered how search engines quickly find the most relevant results from massive datasets? When dealing with billions of high-dimensional vectors, traditional search methods become impractical due to what’s known as high dimensional challenges. In these spaces, data points tend to spread out, making it difficult to efficiently identify nearest neighbors. This is where vector search algorithms come into play, employing innovative scalability strategies to overcome these issues. These algorithms aim to balance accuracy and speed, ensuring that searches remain feasible even as datasets grow exponentially.
Discover how advanced vector search algorithms handle billions of high-dimensional data points efficiently and accurately.
One prominent approach is the Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) algorithm. HNSW constructs a layered graph where each node represents a data point, and edges connect similar points within multiple levels of the hierarchy. This structure allows you to navigate from coarse to fine details quickly, markedly reducing search time. The key to HNSW’s efficiency is its ability to handle high dimensional challenges by enabling rapid approximate nearest neighbor searches with high recall rates. Its scalability strategies involve dynamically adjusting the number of connections at each layer, which helps it maintain performance as dataset size increases. This layered approach means you don’t need to examine every point, making searches faster without sacrificing too much accuracy. Additionally, HNSW leverages scalability strategies to efficiently manage large datasets and high dimensionality.
Another popular technique is Inverted File (IVF). IVF partitions the dataset into clusters or cells, each representing a subset of vectors. When you perform a search, the algorithm first identifies relevant clusters instead of scanning the entire dataset. This drastically cuts down search space, making it scalable for large-scale applications. The core scalability strategy here is quantization, where vectors are compressed into compact representations, allowing quick indexing and retrieval. IVF is particularly effective in high-dimensional spaces because it reduces the search complexity by focusing only on the most promising clusters, thereby tackling the high dimensional challenges head-on.
Product Quantization (PQ) takes a different route by compressing vectors into smaller codes, enabling fast distance computations during search. Instead of comparing raw vectors directly, PQ compares their compact codes, which speeds up the process tremendously. This approach is especially useful when you need to balance high accuracy with low memory usage. PQ’s scalability strategy involves dividing the vector space into subspaces and quantizing each separately, which keeps the memory footprint manageable even for extremely high-dimensional data. This makes PQ a practical choice for large-scale vector databases, where memory and speed are critical.
In essence, each of these algorithms—HNSW, IVF, and PQ—addresses the high dimensional challenges with unique scalability strategies. They push the boundaries of what’s possible in fast, accurate vector search, ensuring that even the largest datasets remain accessible and manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Vector Search Algorithms Handle Noisy or Incomplete Data?
You can rely on vector search algorithms to be fairly noise robust and handle data incompleteness effectively. They use techniques like approximate matching, dimensionality reduction, and indexing structures to filter out noise and fill gaps in data. This means your searches remain accurate even when data is imperfect, enabling you to find relevant results despite noise robustness challenges or incomplete data, ensuring reliable and efficient search performance.
What Are the Latest Advancements in Vector Search Technology?
Imagine your search is a treasure hunt, and neural embeddings are your map, guiding you swiftly through vast data. Recent advancements include enhanced graph-based indexing that accelerates retrieval, even with complex neural embeddings. Innovations like dynamic indexing adapt to real-time data, improving accuracy. These developments make vector search faster and more precise, helping you find what you need with less effort, just like discovering hidden treasures more efficiently.
How Do These Algorithms Perform With Extremely High-Dimensional Data?
You’ll find that HNSW, IVF, and PQ handle extremely high-dimensional data differently. HNSW adapts well by using layered graphs, while IVF benefits from approximate clustering, and PQ reduces dimensionality through quantization. To improve performance, applying dimensionality reduction techniques helps manage data sparsity, making searches faster and more accurate. Overall, combining these algorithms with dimensionality reduction offers a balanced approach to high-dimensional vector search challenges.
Can Vector Search Algorithms Be Integrated With Machine Learning Models?
You can absolutely integrate vector search algorithms with machine learning models, and doing so unlocks powerful capabilities. Imagine seamless model compatibility, where your algorithms enhance data retrieval and improve accuracy. This integration allows your models to leverage efficient indexing, speeding up searches across high-dimensional spaces. While it may seem complex, the payoff is a smarter, more responsive system that adapts to your needs—making advanced AI applications more accessible than ever.
What Are the Common Challenges Faced in Deploying These Algorithms at Scale?
You might face scalability issues when deploying vector search algorithms at scale, especially as data volume grows. Hardware limitations, like insufficient memory or processing power, can hinder performance. To overcome these challenges, optimize your algorithms, utilize scalable hardware solutions, and consider approximate methods. Ensuring efficient indexing and search strategies helps maintain speed and accuracy despite increased data and hardware constraints.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing between HNSW, IVF, and PQ is like selecting the right tool for a masterpiece. Each algorithm is a different brushstroke, shaping how efficiently you find your data needle in the digital haystack. Think of it as tuning an instrument — the better your choice, the sweeter your results. So, weigh your needs carefully, and let these algorithms be your guiding compass through the vast landscape of vector search, leading you to your treasure with precision and grace.