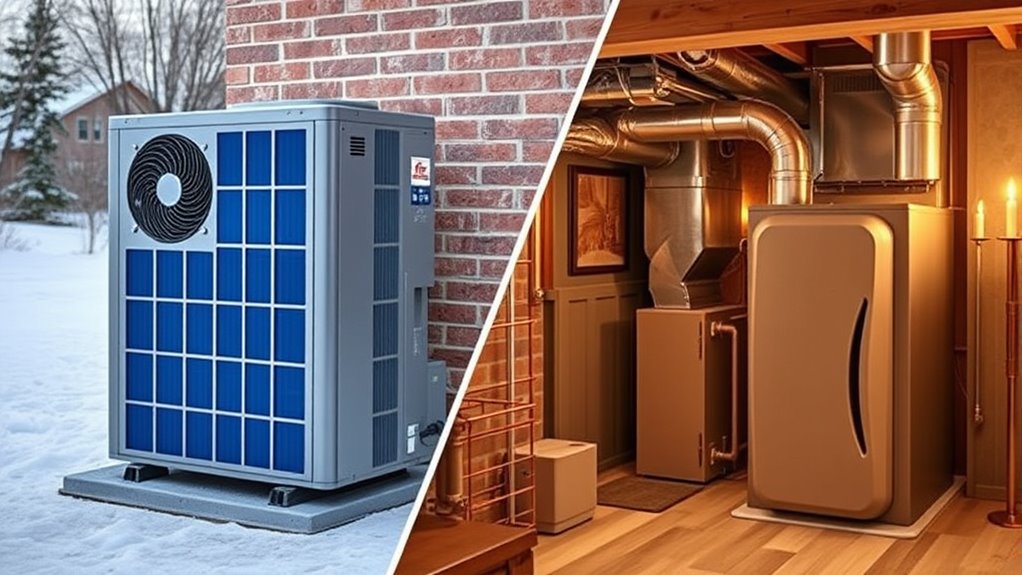
If you’re choosing between a heat pump and a furnace, a heat pump is generally more efficient if you live in a moderate climate since it transfers heat rather than generates it, saving energy and providing both heating and cooling. However, in colder regions, a furnace with high AFUE might perform better. To understand which option suits your needs, consider your climate, costs, and safety factors—more details can help you make the best choice.
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps are more energy-efficient in moderate climates, delivering up to three times more heating energy per unit of electricity.
- Gas furnaces with high AFUE ratings are typically more effective and efficient in extremely cold temperatures.
- Operating costs favor heat pumps due to lower energy consumption, especially in areas with moderate weather.
- Traditional heat pumps lose efficiency at low temperatures, making furnaces more reliable during harsh winters.
- Advanced cold-climate heat pumps improve efficiency, but overall, furnaces are often more efficient in severe winter conditions.
When choosing between a heat pump and a furnace for your home heating needs, understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision. Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient than furnaces, especially in moderate climates, because they transfer heat from the outside air rather than generate it directly. This transfer process allows heat pumps to deliver more energy than they consume, making them up to three times more efficient than traditional systems like gas furnaces. In warmer weather, they can also provide cooling, adding to their versatility. However, in colder climates, high-efficiency gas furnaces might be more effective since heat pumps struggle to operate efficiently at extremely low temperatures. Gas furnaces, especially those with an AFUE of 98.5%, generate heat directly through combustion, which can be more reliable in harsh winter conditions.
Cost is an important factor when selecting a heating system. Heat pumps tend to have higher upfront costs, ranging from $3,500 to $20,000, compared to furnaces, which can cost between $2,000 and $24,000. However, operating costs usually favor heat pumps because they use less electricity or fuel over time. Both systems may qualify for tax credits or rebates, which can offset initial expenses. The overall long-term costs depend on local energy prices, system lifespan, and installation factors, such as your home’s existing infrastructure. Installing a heat pump might require modifications if your home isn’t already prepared for it, impacting costs.
Climate suitability plays a vital role in choosing between these systems. Heat pumps perform best in moderate or warmer climates, where their efficiency is maximized, and they can provide both heating and cooling. Some advanced models are designed to work effectively in colder environments, but traditional heat pumps tend to lose efficiency as temperatures drop. Conversely, furnaces excel in colder climates, reliably providing heat even in extreme conditions. Gas furnaces are specifically designed to produce high heat output quickly, making them a dependable choice for harsh winters.
Safety is another consideration. Gas furnaces pose risks like gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning, requiring proper installation and regular maintenance. Heat pumps, which operate using electricity and refrigerants, are generally safer, with fewer risks associated with combustion. Both systems come equipped with safety features like shut-off switches and pressure regulators, but routine maintenance is essential to guarantee safety, efficiency, and longevity. Additionally, advancements in remote monitoring technology make it easier to ensure system safety and efficiency over time. While heat pumps might have slightly higher maintenance costs due to their complex components, their environmental benefits and safety advantages make them appealing options for many homeowners.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which System Has Lower Long-Term Maintenance Costs?
You want to know which system has lower long-term maintenance costs. Generally, furnaces tend to be more affordable to maintain over time because they need less frequent servicing, fewer replacement parts, and simpler upkeep. Heat pumps, while more efficient, require maintenance twice a year, which can increase costs. So, if minimizing maintenance expenses is your priority, a furnace usually offers a more budget-friendly long-term option.
How Do Installation Costs Compare Between Heat Pumps and Furnaces?
Think of installation costs as building a foundation for your home. You’ll find that heat pumps, especially geothermal ones, tend to be like constructing a grand mansion—more expensive upfront, ranging from $6,000 to $25,000. Furnaces, on the other hand, are like a cozy cottage—more affordable, usually between $1,600 and $9,700. Your choice depends on your climate, home size, and budget, affecting long-term savings.
Are Heat Pumps Effective in Extremely Cold Climates?
You might wonder if heat pumps work well in extremely cold climates. Modern cold-climate heat pumps can operate effectively down to -15°F, with some models even below 0°F. They use advanced features like variable-speed compressors and self-defrost cycles to maintain efficiency and capacity. While they may lose some efficiency in extreme cold, these models are designed to handle harsh conditions, making them a viable option for cold climates.
Can a Heat Pump Replace a Furnace Entirely?
They say, “Don’t put all your eggs in one basket,” but a heat pump might replace a furnace entirely in your home. Modern heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile choice. However, their effectiveness depends on your climate. If you live in a colder region, supplemental heating may still be necessary. Assess your climate and needs before making the switch.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Each Heating System?
You should know that heat pumps markedly reduce environmental impacts compared to traditional furnaces. They cut emissions by up to 93% over 15 years, produce lower greenhouse gases, and rely increasingly on cleaner, renewable energy sources. In contrast, gas furnaces emit CO2 and methane continuously, contributing to climate change and local pollution. Switching to heat pumps helps you lower your carbon footprint and supports a healthier environment over time.
Conclusion
So, as you weigh your options, remember that sometimes the most efficient choice depends on your unique situation. You might find that a heat pump’s versatility aligns perfectly with your needs, or perhaps a furnace’s reliability feels more right. It’s funny how, in the end, the best decision often comes down to what feels like a coincidence—just the right fit at the right time. Trust your gut; your ideal heating solution might be closer than you think.










