A manual transfer switch safely connects your home’s circuits to a backup generator, preventing dangerous backfeeding and electrical shocks. Pros wish more people knew it requires proper installation, load management, and regular testing to work reliably. It’s important to follow safety protocols, like turning off utility power before switching and avoiding overloads. If you’re curious about how to use and maintain one properly, there’s plenty more to uncover to keep your system safe and effective.
Key Takeaways
- Properly size and install the switch to match your generator’s capacity and avoid overloads or safety hazards.
- Always disconnect utility power before switching to generator mode to prevent backfeeding and electric shock.
- Use ergonomic handles and safety features like arc-extinguishing components for safe manual operation.
- Balance load circuits evenly to prevent overloading and ensure reliable power transfer.
- Regularly inspect, test, and follow manufacturer guidelines to maintain safe, efficient transfer switch operation.
Understanding the Core Purpose of Manual Transfer Switches
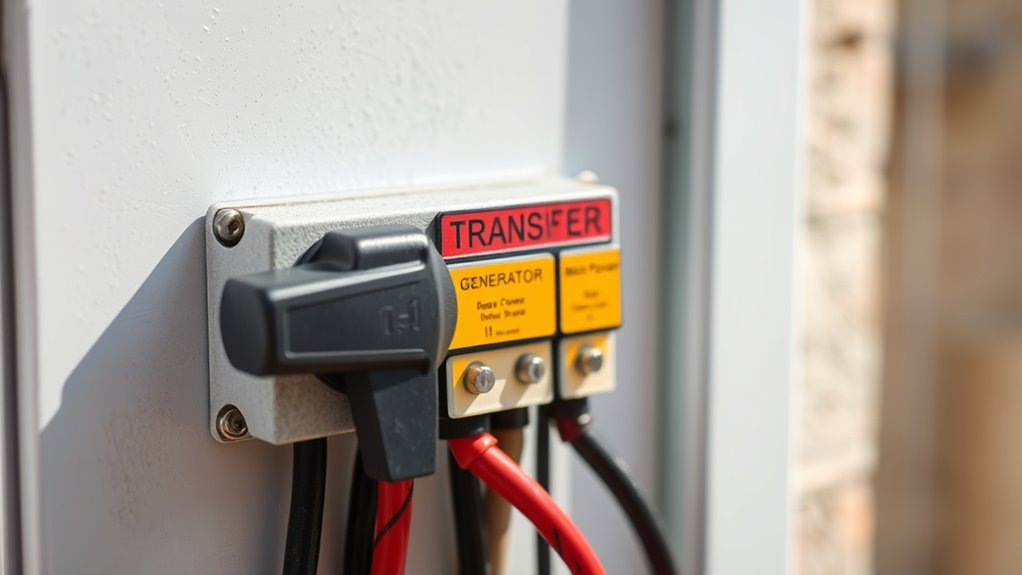

Manual transfer switches serve a critical role in safely switching your home’s power source during outages. Their main function is to connect your electrical circuits to a backup generator, ensuring you maintain power when utility supply fails. You need to operate the switch manually, flipping it from utility to generator power, usually near your main electrical panel for easy access. This setup allows you to selectively power circuits based on your generator’s capacity, avoiding overloads. Using a manual transfer switch is safer than extension cords, reducing fire and electrocution risks. Before switching, you start the generator to ensure a stable supply, then turn off the main utility breaker to prevent backfeeding. A manual transfer switch is connected directly to your home’s electrical system, providing a controlled and safe method to switch sources. This controlled process keeps your home and utility workers safe during power interruptions. Additionally, understanding the importance of proper installation and adhering to local electrical codes is vital for safe and effective operation.
Key Components and How They Contribute to Safety
Safety is built into the design of transfer switches through key components that prevent dangerous conditions during operation. Mechanical interlocks, like molded case circuit breakers, ensure you can’t connect utility and generator power simultaneously, preventing backfeeding. Cam-style male connectors provide secure, reliable connections that maintain safety integrity, unlike Kirk-locks. Mechanical interlocks physically block incompatible connections, eliminating short circuits and energizing utility lines during outages. Electrical interlocks verify that conditions are correct before switching, protecting both you and your equipment. Permanently affixed instructions guide proper operation, reducing user errors. Load management features, such as wattage meters, help you monitor and prevent overloads that could cause fires or damage. Proper enclosures rated for environmental protection and sealed with UL-listed materials safeguard components from moisture and dust, further enhancing safety. Proper installation procedures also help ensure the transfer switch operates safely and reliably over time.
Proper Installation Practices for Reliable Operation
Proper installation of your transfer switch is essential for reliable operation and safety. Begin by choosing an indoor location within 12 inches of the main panel to simplify wiring and use the included flexible conduit. Mount the switch vertically on a sturdy surface, either flush or surface-mounted, ensuring secure fastening with appropriate hardware. Turn off main power before wiring, then connect the armored cable from the switch to the main panel, making sure ground and neutral wires attach correctly to their bus bars. Inside the switch, connect hot wires properly, and verify that circuits suited for generator backup are correctly rewired. Install the weatherproof power inlet box outside for easy generator hookup, sealing it properly to prevent weather damage. Ensuring compatibility between the switch and generator wattage is crucial for safe operation. Finally, test the system thoroughly to confirm safe, reliable operation.
When and How to Use a Manual Transfer Switch Effectively
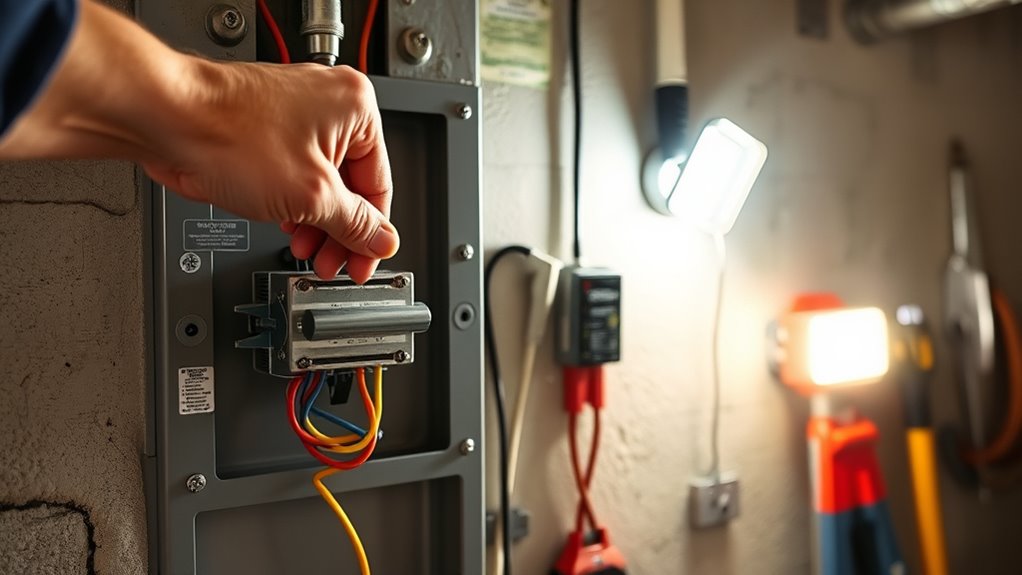

To use your manual transfer switch effectively, you need to understand the proper timing and procedures for switching power sources. Always turn on the generator fully before connecting it, and switch back to utility power only after ensuring the generator is off. Following safety precautions, like disconnecting power cords and confirming power is off, helps prevent accidents and equipment damage. Connecting the generator last ensures that power flows correctly and safely during operation. Additionally, familiarizing yourself with transfer-switch fundamentals can help you operate your system more confidently and prevent potential hazards.
Proper Operation Procedures
Using a manual transfer switch effectively requires following a clear sequence of steps to guarantee safety and reliability. First, confirm your generator is properly fueled, then start it and let it stabilize. Locate it outdoors in a well-ventilated area to prevent exhaust hazards. Turn off the main utility breaker before switching to generator power to avoid backfeeding. Ensure the generator is running before disengaging utility power. Flip the transfer switch to the generator position only after utility power is off. It is also important to understand the essential oils that support safe and effective operation during emergencies. Always monitor loads and disconnect the generator safely after use.
Timing for Switching
Knowing the right moment to switch your manual transfer switch can prevent unnecessary power interruptions and equipment damage. Wait until you’ve confirmed a utility outage before switching to generator power. Start the generator first to ensure it’s stable, then turn off the main utility breaker to prevent backfeeding. Avoid switching during load surges to prevent breaker trips or damage. Delay switching for heavy inductive loads, like air conditioners, by 10-20 seconds to let inrush currents settle. For sensitive equipment, give them time to shut down gracefully before transfer. When switching back to utility, confirm power is stable, then turn off the generator before reconnecting. Perform transfers during low-demand periods when possible, and regularly test your system to optimize timing and reliability. Security considerations also suggest ensuring your system is protected from cyber threats that could disrupt proper transfer operations.
Safety Precautions to Follow
Ensuring safety when operating a manual transfer switch is vital to prevent electrical shocks, equipment damage, and other hazards. Always wear insulating rubber gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself from shocks and burns. Operate the switch with dry hands, and guarantee the area around the switch is dry; avoid standing on wet surfaces or in water. Handle live electrical parts carefully, and never exceed the switch’s maximum load rating to prevent fires or damage. Before switching, turn off the main utility breaker to eliminate backfeed risks and confirm the generator is running properly. Regular inspections for damage and loose connections are essential. Use a licensed electrician for installation and maintenance, and follow all local electrical codes to ensure safe, reliable operation. Additionally, understanding the proper types of headphone jacks can help prevent accidental disconnections or damage when troubleshooting audio issues during setup or maintenance.
Safety Features That Protect Users and Equipment

Safety features in manual transfer switches are essential for protecting both users and equipment during operation. Mechanical and electrical interlocks prevent simultaneous connection of normal and emergency power sources, avoiding dangerous backfeed conditions. These interlocks lock main contacts in either normal or emergency positions, preventing accidental switching under load. These interlocks are often designed to include preventive safety mechanisms that automatically engage under fault conditions, further enhancing user protection. The design includes over-center linkage for quick, secure contact transfer, minimizing arcing and hazards. Switches lacking interlocks, like those with simple circuit breakers, pose safety risks. Certifications such as UL 1008 and compliance with seismic standards ensure safety and durability. Properly designed manual operators, with ergonomic handles and tactile feedback, allow safe switching under full load. Interlocks are critical for preventing accidental contact transfer and integrated arc-extinguishing features like magnetic blowouts further protect users and equipment from electrical faults.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

One common mistake is selecting the wrong circuit for your transfer switch, which can lead to unsafe operation or equipment damage. Skipping safety procedures during installation or manual switching increases the risk of electric shock or equipment failure. To avoid these issues, always follow manufacturer guidelines and prioritize safety at every step. Additionally, choosing a transfer switch with the appropriate electrical specifications for your power sources and loads is crucial to ensure reliable and safe operation. Being aware of the proper transfer procedures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure seamless power transitions.
Improper Circuit Selection
Choosing the wrong circuits for your manual transfer switch is a common mistake that can lead to overloads, tripped breakers, and system failures. If you select more circuits than the switch can handle, you risk overloading your generator and causing outages. Including high-wattage or non-essential circuits, like central air, can overtax your system. Misaligning 15-amp and 20-amp circuits causes compatibility issues or trips. Don’t forget that double-pole 240-volt circuits need two switch slots, and uneven load distribution can overload one side. Proper circuit selection requires matching the transfer switch’s amperage and wattage to your generator and appliances. Prioritize critical loads, like refrigerators and medical equipment, and balance loads evenly to ensure reliable, safe operation during outages. Matching the transfer switch’s capacity to your total load is essential to prevent potential hazards and ensure a smooth power transfer. Additionally, understanding proper wiring and grounding practices can help prevent safety issues and ensure system longevity.
Neglecting Safety Procedures
Neglecting safety procedures when operating a manual transfer switch can lead to serious injuries or equipment damage. Never operate the switch while standing in water or on wet surfaces, as this greatly increases the risk of electrocution. Always disconnect the main power before switching to prevent accidental shocks. Use personal protective equipment like rubber gloves and safety glasses, and operate the switch with dry hands in a dry environment. Only qualified electricians should inspect, maintain, or repair the switch to guarantee safety around live parts. Regular inspections, proper installation, and adherence to safety protocols are essential. Failing to follow these steps can result in electrical faults, fires, or injuries, compromising your safety and that of your equipment. Stay vigilant, prioritize safety, and stay protected. Additionally, understanding the risks of improper wiring or maintenance can help prevent dangerous situations and ensure the long-term reliability of your backup power system. To further mitigate hazards, always be aware of safety procedures and follow manufacturer guidelines diligently.
Maintenance Tips to Maximize Longevity and Performance

Regular maintenance is essential to guarantee your manual transfer switch operates reliably and lasts longer. Start with weekly visual inspections inside the enclosure, looking for dust, debris, moisture, or corrosion. Use a vacuum or microfiber cloth to remove contaminants—avoid blowers that can lodge debris into sensitive parts. Check for loose, damaged, or worn components, and ensure covers and barriers are securely fastened. Lubricate moving parts and contacts with manufacturer-approved lubricants, but don’t overdo it. Manually operate the switch to verify smooth movement and proper contact. Perform monthly load testing to confirm proper operation during power transfer, including generator testing. Tighten wiring connections, inspect insulation, and verify grounding regularly. Keep detailed records and schedule annual professional inspections to maintain excellent performance and safety.
Choosing the Right Manual Transfer Switch for Your Needs

Selecting the right manual transfer switch involves understanding your specific electrical system requirements and safety considerations. First, determine whether you need a 3-pole or 4-pole configuration to match your system’s voltage and grounding. Check that the switch’s current rating (typically between 60 and 1200A) suits your load demands, and ensure it’s UL listed for safety. Consider switches with drawout mounts for easier maintenance. Pay attention to enclosure ratings—NEMA Type 1, 3R, or 4X—to match your environment’s dust or water exposure. Safety features like interlocked manual operators, safety handles, and visual status indicators are essential. Compatibility with your generator type and circuit breaker panel simplifies installation. Lastly, verify that the switch’s wiring, fuse ratings, and installation meet local electrical codes for reliable, safe operation. Additionally, assessing the switch’s compliance with safety standards can help prevent potential hazards during operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Install a Manual Transfer Switch Myself?
You shouldn’t install a manual transfer switch yourself unless you’re a qualified electrician. It involves complex wiring, turning off main power, and adhering to strict safety codes. Mistakes can cause electrocution, fire hazards, or damage your electrical system. Hiring a licensed professional guarantees the installation is safe, legal, and up to code. Plus, many insurance policies require professional installation to cover any damages or issues.
What Circuits Should I Prioritize During an Outage?
During an outage, you should first power crucial circuits like medical equipment, security systems, and communication devices—they’re your lifelines. Then, switch on refrigeration, heating, and water pumps to keep essentials running smoothly. Don’t forget smoke detectors and fire alarms for safety. Carefully balance your load to avoid overloading the generator. Prioritize these essential circuits to stay safe, secure, and comfortable until power is restored.
How Often Should I Test My Manual Transfer Switch?
You should test your manual transfer switch monthly by operating it from primary to backup and back to guarantee proper functioning. Additionally, conduct a load test lasting at least 30 minutes once a month to verify system performance under real conditions. Complement this with weekly visual inspections for dirt, damage, or wear. Annual thorough tests are also essential to confirm timing and safety features meet standards.
Is a Manual Transfer Switch Suitable for Large Power Loads?
A picture is worth a thousand words, and the same applies to your power system. Yes, a manual transfer switch suits large power loads if it’s rated for your specific amperage, like 200 to 1200 amps, and properly installed by professionals. It provides reliable control for industrial or commercial needs, especially when matched with high-capacity models for large, critical loads, ensuring safe and seamless power transfer during outages.
What Safety Precautions Are Necessary During Switching Operations?
During switching operations, you must wear insulated rubber gloves and safety glasses to prevent shocks and burns. Make sure your hands are dry, and stand on a dry surface, away from water or conductive liquids. Turn off the main utility breaker before switching to generator power, and confirm the generator is stable and off before returning to utility power. Keep children away and monitor the system closely for safety.
Conclusion
Think of your manual transfer switch as the steady anchor in a stormy sea—keeping your power safe and reliable. By understanding its core purpose, installing it correctly, and practicing proper use, you’re steering clear of dangerous waters. Regular maintenance and smart choices guarantee it acts as your loyal lighthouse, guiding you safely through power outages. When you respect its power and follow best practices, your home’s energy lifeline stays strong and unwavering.










